I have often written about learning styles and how each person can relate to material presented in certain ways better than they can grasp the same material presented in other ways. Today’s lesson is for the parent who is saying, “Okay, I understand that this child is more auditory and that child is more visual, but what do I do with that information?” I will walk you through a basic lesson for early math, skip-counting. While giving you some tips for teaching skip-counting, I will also show you how to adapt any lesson to cover each of the various learning styles. Covering all learning styles in a lesson will enable all of your students to learn the material at the same time and give each student a more complete understanding of the material being presented.
Begin by explaining the principle of skipping to your child: walk across the room with him, then skip across the room with him to illustrate how skipping covers the same distance faster and requires fewer steps than merely walking does. Explain that skip-counting is a short-cut way to count things, by using fewer steps and skipping over certain numbers to cover the distance faster.
Children love kinesthetic applications, so if the weather allows, let’s take the math outside. Use sidewalk chalk to draw a long line down the sidewalk or driveway. Now mark the line off in reasonable increments (approximately the length of your child’s foot) and number each mark to create a number line so that your child can step from number to number. Drawing this as a long row of numbered boxes (instead of just a thin line) might make the concept easier for your child to understand, as it will resemble a giant game board where he can jump from box to box. Have him stand at the beginning (make a “start” or “zero” place), then have him step or jump to the “2” place, then to 4, and then to 6 to show him the concept of counting by two’s. Can he tell you where he should go next?
Once he is able to skip-count by 2’s, you can repeat the activity by having him skip-count by 4’s. If the increments become too large to step or jump to, he can run quickly across the “skipped” numbers and stop on the desired number, shouting the number loudly as he skip-counts the increments. If numbered boxes on the sidewalk do not work for your situation, try using kitchen floor tiles or stairs, or use masking tape to “mark” a line on your floor or carpeting.
Next, shift the concept from kinesthetic to tactile by drawing a series of smaller numbered boxes on paper and have him do “finger skipping” from one number to another, first by 1’s, then by 2’s. You may eventually want to let him use some game pawns, moving them from square to square while counting off the increments.
When your child understands the entire concept of skip-counting, you can pour out a large quantity of the substance of your choice onto the table (or a cookie sheet) and allow your student to start counting objects: M&M’s, oyster crackers, dry beans, buttons, Lego’s, or checkers. Count them by 1’s until he has the idea that counting them all individually will be a long process. Now have him move two at a time and try counting by 2’s. Allow him some time to practice this concept — it can be difficult to do any task until you are used to it. After he has the 2’s mastered, then you can move on to skip-counting by 4’s, 3’s, 5’s, 10’s, or any desired increment. (Counting by 4’s is an easy concept to follow counting by 2’s, since it is just a larger extension of counting by 2’s — counting just the even numbers by 2’s. I recommend doing the 4’s before the 3’s for this reason. In the same manner, follow counting by 3’s with 6’s, and follow 5’s with 10’s.)
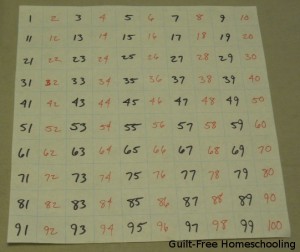
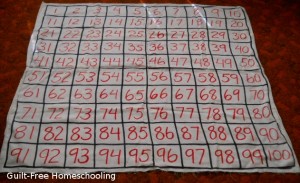
Another activity to help a student understand skip-counting by 2’s is to fill in a 100-chart with colored markers (adding a strong visual element). Draw* a chart of 10 x 10 boxes (10 rows of 10 squares each). Now alternate filling in the numbers: Mom writes an odd number in black, and the student writes an even number in red. Say each number aloud (here is the auditory part of the lesson) as you write them. Read the numbers over again when the chart is all filled in, alternating as Mom says a number she wrote and the student says a number he wrote — and suddenly the student is counting by 2’s! Then Mom can be quiet while he reads only his numbers aloud to reinforce his new skill. (Adapt this activity to other increments as needed for skill in skip-counting.) *Note: 1-inch graph paper is available at office supply stores in a poster-sized display tablet. I LOVE THIS STUFF! It is great for fast number charts — and hundreds of other homeschool uses. I rolled mine up and tied the roll securely with string for easier storage on a closet shelf.
Graph paper marked with five squares per inch (also available in office supply stores) can be used to make a measuring tape for math as a good tactile and visual learning aid. Cut a few sheets into 1-inch wide strips and tape them together for the length you desire. This scale is compatible with the centimeter-scale Cuisenaire Rods: 2 graph-squares = 1 centimeter, so marking numbers on every other line produces a centimeter measuring tape. I used it to illustrate multiplication and division facts by accordion-folding the paper tape into 6 sections of 8 centimeters to show 6 x 8 = 48 and other facts, but a similar principle will work for skip-counting. Fold the tape on every other number, and then read off (auditory) the numbers at each fold for skip-counting by 2’s. Adapt and repeat for other increments.
When your student has advanced to skip-counting by 10’s, draw a large 100-chart on the driveway, and your student can jump or run from box to box (kinesthetic), or have him fill in the numbers with colored chalk (tactile & visual). Do the 100-chart activity on paper with red numbers on the 10’s only (tactile & visual), but black numbers on the other squares. Then write 1-10 in a vertical column on paper, saying them aloud (auditory). Now add a zero to each number, and read aloud again to count by 10’s. Repeat, adding more zeroes, to count by 100’s, 1,000’s, 10,000’s, or as many zeroes as your child can handle.
Kinesthetic teaching tactics will involve large muscle groups: moving arms from the shoulders or moving legs from the hips. Walking, hopping, running, and jumping, and throwing, catching, and reaching are excellent ways to teach a kinesthetic child. You want to have him move his entire body whenever possible. If a child is easily distracted while trying to sit still, he is probably a kinesthetic learner. If the lesson takes place while the student is seated, it is probably not a kinesthetic lesson. If you want a kinesthetic child to learn, do not try to keep his bottom stuck to a chair seat. Let him stand, let him walk around, let him throw a ball to you while reciting, if necessary, but incorporate his need for movement into your lessons. (Notice that this is not wiggling and moving around just for the sake of wiggling and moving and trying to disturb others. This is taking in information through well-coordinated muscles and reinforcing it through repeated muscular actions.)
Tactile teaching tactics will involve small muscle groups: moving hands from the wrist, moving fingers, and touching, feeling, and rubbing with fingertips. Textures, from dramatic and rough to subtle and smooth, and finger and hand movements are excellent ways to teach a tactile child. You want to have him touching something related to the lesson whenever possible. If a child is easily distracted while trying to keep his hands still, he is probably a tactile learner. If the lesson takes place while the student’s hands are empty, it is probably not a tactile lesson. If you want a tactile child to learn, do not try to keep his hands empty and quiet. Let him touch things, let him make something, let him hold a toy while reciting, if necessary, but incorporate his need for touching into your lessons. (Notice that this is not touching and fiddling with things just for the sake of touching and fiddling and trying to disturb others. This is taking in information through an acute sense of touch and reinforcing it through repetitive touches.)
Auditory teaching tactics will involve sound: incoming sounds and outgoing sounds. Speaking, singing, and humming, and listening are all ways to teach an auditory child. You want to involve his ears and vocal chords whenever possible. If a child is easily distracted while the room is quiet, he is probably an auditory learner. If the lesson requires the student to read quietly, it is probably not an auditory lesson. If you want an auditory child to learn, do not try to keep him quiet. Let him hum, let him sing, let him read his assignments aloud, let him discuss the lessons with you, let him listen to music in the background, if necessary, but incorporate his need for vocalization into your lessons. (Notice that this is not making noise just for the sake of making noise and trying to disturb others. This is taking in information through highly sensitive ear-gates and reinforcing it through vocal repetition.)
Visual teaching tactics will involve illustrations and colors: graphs, charts, and diagrams, and lots of bright, stimulating colors. Posters, maps, forms, and worksheets, and color-coding are excellent ways to teach a visual child. You want to involve his eyes whenever possible. If a child is easily distracted while listening, but is not bothered by sitting still, he is probably a visual learner. If the lesson takes place while the student has no examples to look at, it is probably not a visual lesson. If you want a visual child to learn, do not try to keep his eyes focused on you. Let him read, let him draw, let him color while you read aloud, if necessary, but incorporate his need for visual details into your lessons. (Notice that this is not looking around and daydreaming just for the sake of looking and daydreaming and trying to disturb others. This is taking in information through very observant eye-gates and reinforcing it through recalling memory-pictures.)
Any lesson can be adapted to include elements of the various learning styles. Do not be afraid to be creative in trying revolutionary approaches that seem to be unusual applications for the subject at hand. Your “crazy idea” may be the exact key that unlocks the door to learning for your students.












 Guilt-Free Homeschooling is the creation of Carolyn Morrison and her daughter, Jennifer Leonhard. After serious disappointments with public school, Carolyn spent the next 11 years homeschooling her two children, from elementary to high school graduation and college admission. Refusing to force new homeschooling families to re-invent the wheel, Carolyn and Jennifer now share their encouragement, support, tips, and tricks, filling their blog with "all the answers we were looking for as a new-to-homeschooling family" and making this website a valuable resource for parents, not just a daily journal. Guilt-Free Homeschooling -- Equipping Parents for Homeschooling Success!
Guilt-Free Homeschooling is the creation of Carolyn Morrison and her daughter, Jennifer Leonhard. After serious disappointments with public school, Carolyn spent the next 11 years homeschooling her two children, from elementary to high school graduation and college admission. Refusing to force new homeschooling families to re-invent the wheel, Carolyn and Jennifer now share their encouragement, support, tips, and tricks, filling their blog with "all the answers we were looking for as a new-to-homeschooling family" and making this website a valuable resource for parents, not just a daily journal. Guilt-Free Homeschooling -- Equipping Parents for Homeschooling Success!

Recent Comments